Pulmonary Emboli on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (
 About 90% of emboli are from
About 90% of emboli are from
 To diagnose a pulmonary embolism, a review of clinical criteria to determine the need for testing is recommended. In those who have low risk, age less than 50, heart rate less than 100 beats per minute, oxygen level more than 94% on room air, and no leg swelling, coughing up of blood, surgery or trauma in the last four weeks, previous blood clots, or estrogen use, further testing is not typically needed.
In situations with more high risk individuals, further testing is needed. A
To diagnose a pulmonary embolism, a review of clinical criteria to determine the need for testing is recommended. In those who have low risk, age less than 50, heart rate less than 100 beats per minute, oxygen level more than 94% on room air, and no leg swelling, coughing up of blood, surgery or trauma in the last four weeks, previous blood clots, or estrogen use, further testing is not typically needed.
In situations with more high risk individuals, further testing is needed. A
File:Computed tomograph of pulmonary vessels.jpg, On CT scan, pulmonary emboli can be classified according to the level along the arterial tree.
File:SegandSubsegPE.png, Segmental and subsegmental pulmonary emboli on both sides
File:Pulmonary embolism CTPA.JPEG,
Assessing the accuracy of CT pulmonary angiography is hindered by the rapid changes in the number of rows of detectors available in multidetector CT (MDCT) machines. According to a
 A
A
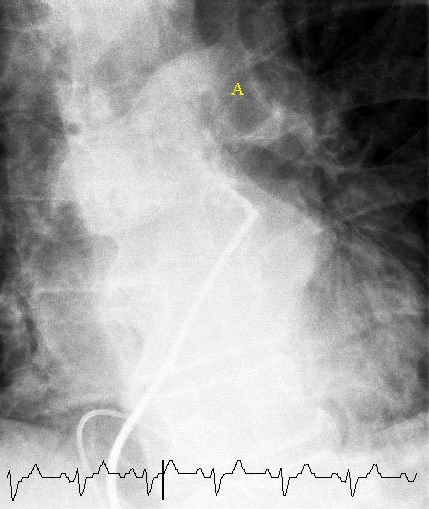 Historically, the
Historically, the
 The primary use of the ECG is to rule out other causes of chest pain. An electrocardiogram (ECG) is routinely done on people with chest pain to quickly diagnose
The primary use of the ECG is to rule out other causes of chest pain. An electrocardiogram (ECG) is routinely done on people with chest pain to quickly diagnose

File:UOTW 2 - Ultrasound of the Week 1.webm, Ultrasound of the heart showing signs of PE
File:UOTW 2 - Ultrasound of the Week 2.webm, Ultrasound of the heart showing signs of PE
 There are two situations when an
There are two situations when an
 Fewer than 5 to 10% of symptomatic PEs are fatal within the first hour of symptoms.
There are several markers used for risk stratification and these are also independent predictors of adverse outcomes. These include hypotension, cardiogenic shock, syncope, evidence of right heart dysfunction, and elevated cardiac enzymes. Some ECG changes including S1Q3T3 also correlate with a worse short-term prognosis. There have been other patient-related factors such as
Fewer than 5 to 10% of symptomatic PEs are fatal within the first hour of symptoms.
There are several markers used for risk stratification and these are also independent predictors of adverse outcomes. These include hypotension, cardiogenic shock, syncope, evidence of right heart dysfunction, and elevated cardiac enzymes. Some ECG changes including S1Q3T3 also correlate with a worse short-term prognosis. There have been other patient-related factors such as
Wells criteria for pulmonary embolism online calculator
Clinical prediction website – Wells criteria for pulmonary embolism
* * {{Authority control Medical emergencies Pulmonary heart disease and diseases of pulmonary circulation Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate
embolism
An embolism is the lodging of an embolus, a blockage-causing piece of material, inside a blood vessel. The embolus may be a blood clot (thrombus), a fat globule ( fat embolism), a bubble of air or other gas (gas embolism), amniotic fluid (amniot ...
). Symptoms of a PE may include shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing disc ...
, chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
particularly upon breathing in, and coughing up blood. Symptoms of a blood clot in the leg may also be present, such as a red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
, warm, swollen, and painful leg. Signs of a PE include low blood oxygen levels, rapid breathing
Tachypnea, also spelt tachypnoea, is a respiratory rate greater than normal, resulting in abnormally rapid and shallow breathing.
In adult humans at rest, any respiratory rate of 1220 per minute is considered clinically normal, with tachypnea b ...
, rapid heart rate, and sometimes a mild fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a body temperature, temperature above the human body temperature, normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point. There is not a single ...
. Severe cases can lead to passing out Passing may refer to:
Social identity
* Passing (sociology), presenting oneself as a member of another sociological group
** Passing (gender), presenting oneself as being cisgender
** Passing (racial identity), presenting oneself as a member of ...
, abnormally low blood pressure, obstructive shock
Obstructive shock is one of the four types of shock, caused by a physical obstruction in the flow of blood. Obstruction can occur at the level of the great vessels or the heart itself. Causes include pulmonary embolism, cardiac tamponade, and tensi ...
, and sudden death.
PE usually results from a blood clot in the leg that travels to the lung. The risk of blood clot
A thrombus (plural thrombi), colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of c ...
s is increased by advanced age, cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
, prolonged bed rest
Bed rest, also referred to as the rest-cure, is a medical treatment in which a person lies in bed for most of the time to try to cure an illness. Bed rest refers to voluntarily lying in bed as a treatment and not being confined to bed because of ...
and immobilization, smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is typically breathed in to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have bee ...
, stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
, long-haul travel
Travel is the movement of people between distant geographical locations. Travel can be done by foot, bicycle, automobile, train, boat, bus, airplane, ship or other means, with or without luggage, and can be one way or round trip. Travel c ...
over 4 hours, certain genetic conditions, estrogen-based medication, pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ca ...
, obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's we ...
, trauma or bone fracture
A bone fracture (abbreviated FRX or Fx, Fx, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any bone in the body. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a '' ...
, and after some types of surgery. A small proportion of cases are due to the embolization
Embolization refers to the passage and lodging of an embolus within the bloodstream. It may be of natural origin (pathological), in which sense it is also called embolism, for example a pulmonary embolism; or it may be artificially induced (t ...
of air
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing f ...
, fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers spec ...
, or amniotic fluid
The amniotic fluid is the protective liquid contained by the amniotic sac of a gravid amniote. This fluid serves as a cushion for the growing fetus, but also serves to facilitate the exchange of nutrients, water, and biochemical products betwee ...
. Diagnosis is based on signs and symptoms in combination with test results. If the risk is low, a blood test known as a D-dimer
D-dimer (or D dimer) is a fibrin degradation product (or FDP), a small protein fragment present in the blood after a blood clot is degraded by fibrinolysis. It is so named because it contains two D fragments of the fibrin protein joined by a cross ...
may rule out the condition. Otherwise, a CT pulmonary angiography
A CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) is a medical diagnostic test that employs computed tomography (CT) angiography to obtain an image of the pulmonary arteries. Its main use is to diagnose pulmonary embolism (PE). It is a preferred choice of imaging i ...
, lung ventilation/perfusion scan
A ventilation/perfusion lung scan, also called a V/Q lung scan, or ventilation/perfusion scintigraphy, is a type of medical imaging using scintigraphy and medical isotopes to evaluate the circulation of air and blood within a patient's lungs, in o ...
, or ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequency, frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing range, hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hea ...
of the legs may confirm the diagnosis. Together, deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enla ...
and PE are known as venous thromboembolism
Venous thrombosis is blockage of a vein caused by a thrombus (blood clot). A common form of venous thrombosis is deep vein thrombosis (DVT), when a blood clot forms in the deep veins. If a thrombus breaks off (embolizes) and flows to the lungs to ...
(VTE).
Efforts to prevent PE include beginning to move as soon as possible after surgery, lower leg exercises during periods of sitting, and the use of blood thinners
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where the ...
after some types of surgery. Treatment is with anticoagulants such as heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Since heparins depend on the activity of antithrombin, they are considered anticoagulants. Specifically it is also used in the treatm ...
, warfarin
Warfarin, sold under the brand name Coumadin among others, is a medication that is used as an anticoagulant (blood thinner). It is commonly used to prevent blood clots such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, and to prevent strok ...
or one of the direct-acting oral anticoagulants (DOACs). These are recommended for at least three months. Severe cases may require thrombolysis
Thrombolysis, also called fibrinolytic therapy, is the breakdown (lysis) of blood clots formed in blood vessels, using medication. It is used in ST elevation myocardial infarction, stroke, and in cases of severe venous thromboembolism (massive p ...
using medication such as tissue plasminogen activator
Tissue plasminogen activator (abbreviated tPA or PLAT) is a protein involved in the breakdown of blood clots. It is a serine protease () found on endothelial cells, the cells that line the blood vessels. As an enzyme, it catalyzes the conversion ...
(tPA) given intravenously or through a catheter, and some may require surgery (a pulmonary thrombectomy
A pulmonary thrombectomy is an emergency surgical procedure used to remove blood clots from the pulmonary arteries.
Mechanical thrombectomies can be surgical (surgical thrombectomy) or percutaneous (percutaneous thrombectomy).
Surgical thrombect ...
). If blood thinners are not appropriate, a temporary vena cava filter
An inferior vena cava filter is a medical device made of metal that is implanted by vascular surgeons or interventional radiologists into the inferior vena cava to
prevent a life-threatening pulmonary embolism (PE) or venous thromboembolism (VTE) ...
may be used.
Pulmonary emboli affect about 430,000 people each year in Europe. In the United States, between 300,000 and 600,000 cases occur each year, which contribute to at least 40,000 deaths. Rates are similar in males and females. They become more common as people get older.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism are typically sudden in onset and may include one or many of the following:dyspnea
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathing, breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of brea ...
(shortness of breath), tachypnea
Tachypnea, also spelt tachypnoea, is a respiratory rate greater than normal, resulting in abnormally rapid and shallow breathing.
In adult humans at rest, any respiratory rate of 1220 per minute is considered clinically normal, with tachypnea be ...
(rapid breathing), chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
of a "pleuritic" nature (worsened by breathing), cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages that can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three pha ...
and hemoptysis
Hemoptysis is the coughing up of blood or blood-stained mucus from the bronchi, larynx, trachea, or lungs. In other words, it is the airway bleeding. This can occur with lung cancer, infections such as tuberculosis, bronchitis, or pneumonia, and ...
(coughing up blood). More severe cases can include signs such as cyanosis
Cyanosis is the change of body tissue color to a bluish-purple hue as a result of having decreased amounts of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Body tissues that show cyanosis are usually in locations ...
(blue discoloration, usually of the lips and fingers), collapse, and circulatory instability because of decreased blood flow through the lungs and into the left side of the heart. About 15% of all cases of sudden death are attributable to PE. While PE may present with syncope, less than 1% of syncope cases are due to PE.
On physical examination, the lungs are usually normal. Occasionally, a pleural friction rub
A pleural friction rub, or simply pleural rub, is an audible medical sign present in some patients with pleurisy and other conditions affecting the chest cavity. It is noted by listening to the internal sounds of the body, usually using a stethosco ...
may be audible over the affected area of the lung (mostly in PE with infarct
Infarction is tissue death (necrosis) due to Ischemia, inadequate blood supply to the affected area. It may be caused by Thrombosis, artery blockages, rupture, mechanical compression, or vasoconstriction. The resulting lesion is referred to as a ...
). A pleural effusion
A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung.
Under normal conditions, pleural fluid is secreted by the parietal pleural capillaries at a rate of 0.6 millilitre per kilog ...
is sometimes present that is exudative, detectable by decreased percussion note, audible breath sounds, and vocal resonance. Strain on the right ventricle may be detected as a left parasternal heave, a loud pulmonary component of the second heart sound, and/or raised jugular venous pressure
The jugular venous pressure (JVP, sometimes referred to as ''jugular venous pulse'') is the indirectly observed pressure over the venous system via visualization of the internal jugular vein. It can be useful in the differentiation of different for ...
. A low-grade fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a body temperature, temperature above the human body temperature, normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point. There is not a single ...
may be present, particularly if there is associated pulmonary hemorrhage or infarction.
As smaller pulmonary emboli tend to lodge in more peripheral areas without collateral circulation, they are more likely to cause lung infarction and small effusions (both of which are painful), but not hypoxia, dyspnea, or hemodynamic instability such as tachycardia. Larger PEs, which tend to lodge centrally, typically cause dyspnea, hypoxia, low blood pressure
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the dia ...
, fast heart rate
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal (su ...
and fainting
Syncope, commonly known as fainting, or passing out, is a loss of consciousness and muscle strength characterized by a fast onset, short duration, and spontaneous recovery. It is caused by a decrease in blood flow to the brain, typically from ...
, but are often painless because there is no lung infarction due to collateral circulation. The classic presentation for PE with pleuritic pain, dyspnea, and tachycardia is likely caused by a large fragmented embolism causing both large and small PEs. Thus, small PEs are often missed because they cause pleuritic pain alone without any other findings and large PEs are often missed because they are painless and mimic other conditions often causing ECG changes and small rises in troponin and brain natriuretic peptide levels.
PEs are sometimes described as massive, submassive, and nonmassive depending on the clinical signs and symptoms. Although the exact definitions of these are unclear, an accepted definition of massive PE is one in which there is hemodynamic instability. This is a cause of obstructive shock, which presents as sustained low blood pressure, slowed heart rate, or pulselessness.
Risk factors
 About 90% of emboli are from
About 90% of emboli are from proximal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
leg deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enla ...
(DVTs) or pelvic vein thromboses. The rare venous thoracic outlet syndrome can also be a cause of DVTs, especially in young men without significant risk factors. DVTs are at risk for dislodging and migrating to the lung circulation. The conditions are generally regarded as a continuum termed ''venous thromboembolism
Venous thrombosis is blockage of a vein caused by a thrombus (blood clot). A common form of venous thrombosis is deep vein thrombosis (DVT), when a blood clot forms in the deep veins. If a thrombus breaks off (embolizes) and flows to the lungs to ...
'' (VTE).
VTE is much more common in immunocompromised individuals as well as individuals with comorbidities including:
* Those that undergo orthopedic surgery at or below the hip without prophylaxis.
** This is due to immobility during or after the surgery, as well as venous damage during the surgery.
* Pancreatic and colon cancer patients (other forms of cancer also can be factors, but these are the most common)
** This is due to the release of procoagulants.
*** Risk of VTE is at its greatest during diagnosis and treatment, but lowers in remission.
* Patients with high-grade tumors
* Pregnant individuals
** As the body puts itself into what is known as a "hypercoagulable state" the risk of a hemorrhage during childbirth is decreased and is regulated by increased expression of factors VII, VIII, X, Von Willebrand, and fibrinogen
Fibrinogen (factor I) is a glycoprotein complex, produced in the liver, that circulates in the blood of all vertebrates. During tissue and vascular injury, it is converted enzymatically by thrombin to fibrin and then to a fibrin-based blood clo ...
.
* Those on estrogen medication
The development of thrombosis is classically due to a group of causes named Virchow's triad
Virchow's triad or the triad of Virchow () describes the three broad categories of factors that are thought to contribute to thrombosis.
*Hypercoagulability
*Hemodynamic changes (stasis, turbulence)
*Endothelial injury/dysfunction
It is named a ...
(alterations in blood flow, factors in the vessel wall, and factors affecting the properties of the blood). Often, more than one risk factor is present.
* ''Alterations in blood flow'': immobilization (after surgery, long-haul flight), injury
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, o ...
, pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ca ...
(also procoagulant), obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's we ...
(also procoagulant), cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
(also procoagulant)
* ''Factors in the vessel wall'': surgery, catheterizations causing direct injury ("endothelial injury")
* ''Factors affecting the properties of the blood'' (procoagulant state):
** Estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal acti ...
-containing medication
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and re ...
(transgender hormone therapy
Transgender hormone therapy, also called hormone replacement therapy (HRT) or gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT), is a form of hormone therapy in which sex hormones and other hormonal medications are administered to transgender or gender nonc ...
, menopausal hormone therapy
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), also known as menopausal hormone therapy or postmenopausal hormone therapy, is a form of hormone therapy used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause. These symptoms can include hot flashes, vagina ...
and hormonal contraceptives
Hormonal contraception refers to birth control methods that act on the endocrine system. Almost all methods are composed of steroid hormones, although in India one selective estrogen receptor modulator is marketed as a contraceptive. The original ...
)
** Genetic thrombophilia (factor V Leiden
Factor V Leiden (rs6025 or ''F5'' p.R506Q) is a variant (mutated form) of human factor V (one of several substances that helps blood clot), which causes an increase in blood clotting (hypercoagulability). Due to this mutation, protein C, an anticoa ...
, prothrombin mutation G20210A
Prothrombin G20210A is a genetic condition that increases the risk of thrombophilia, blood clots including from deep vein thrombosis, and of pulmonary embolism. One copy of the mutation increases the risk of a blood clot from 1 in 1,000 per year t ...
, protein C deficiency
Protein C deficiency is a rare genetic trait that predisposes to thrombotic disease. It was first described in 1981. The disease belongs to a group of genetic disorders known as thrombophilias. Protein C deficiency is associated with an increased ...
, protein S deficiency
Protein S deficiency is a disorder associated with increased risk of venous thrombosis. Protein S, a vitamin K-dependent physiological anticoagulant, acts as a nonenzymatic cofactor to activate protein C in the degradation of factor Va and factor V ...
, antithrombin
Antithrombin (AT) is a small glycoprotein that inactivates several enzymes of the coagulation system. It is a 432-amino-acid protein produced by the liver. It contains three disulfide bonds and a total of four possible glycosylation sites. α-An ...
deficiency, hyperhomocysteinemia
Hyperhomocysteinemia is a medical condition characterized by an abnormally high level of homocysteine in the blood, conventionally described as above 15 μmol/L.
As a consequence of the biochemical reactions in which homocysteine is involved ...
and plasminogen
Plasmin is an important enzyme () present in blood that degrades many blood plasma proteins, including fibrin clots. The degradation of fibrin is termed fibrinolysis. In humans, the plasmin protein (in the zymogen form of plasminogen) is encode ...
/fibrinolysis
Fibrinolysis is a process that prevents blood clots from growing and becoming problematic. Primary fibrinolysis is a normal body process, while secondary fibrinolysis is the breakdown of clots due to a medicine, a medical disorder, or some other c ...
disorders)
** Acquired thrombophilia (antiphospholipid syndrome
Antiphospholipid syndrome, or antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS or APLS), is an autoimmune, hypercoagulable state caused by antiphospholipid antibodies. APS provokes blood clots (thrombosis) in both arteries and veins as well as pregnancy- ...
, nephrotic syndrome
Nephrotic syndrome is a collection of symptoms due to kidney damage. This includes protein in the urine, low blood albumin levels, high blood lipids, and significant swelling. Other symptoms may include weight gain, feeling tired, and foamy ...
, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is a rare, acquired, life-threatening disease of the blood characterized by destruction of red blood cells by the complement system, a part of the body's innate immune system. This destructive process occu ...
)
** Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
(due to secretion of pro-coagulants)
Although most pulmonary embolisms are the result of proximal leg deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enla ...
(DVTs), there are still many other risk factors that can also result in a pulmonary embolism.
* Risk factors include:
** Varicose veins
Varicose veins, also known as varicoses, are a medical condition in which superficial veins become enlarged and twisted. These veins typically develop in the legs, just under the skin. Varicose veins usually cause few symptoms. However, some indi ...
caused by vascular damage
** Pulmonary hypertension
** Diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
** Traumatic hip fractures that immobilize the patient
** Joint fixation (primarily in the legs)
Underlying causes
After a first PE, the search for secondary causes is usually brief. Only when a second PE occurs, and especially when this happens while still underanticoagulant
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where the ...
therapy, a further search for underlying conditions is undertaken. This will include testing ("thrombophilia screen") for Factor V Leiden mutation, antiphospholipid antibodies, protein C
Protein C, also known as autoprothrombin IIA and blood coagulation factor XIX, is a zymogen, that is, an inactive enzyme. The activated form plays an important role in regulating anticoagulation, inflammation, and apoptosis, cell death and ...
and S and antithrombin
Antithrombin (AT) is a small glycoprotein that inactivates several enzymes of the coagulation system. It is a 432-amino-acid protein produced by the liver. It contains three disulfide bonds and a total of four possible glycosylation sites. α-An ...
levels, and later prothrombin mutation, MTHFR
Methylenetetrahydrofolatereductase (MTHFR) is the rate-limiting enzyme in the methyl cycle, and it is encoded by the ''MTHFR'' gene. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase catalyzes the conversion of 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate to 5-methyltetrahyd ...
mutation, Factor VIII
Factor VIII (FVIII) is an essential blood-clotting protein, also known as anti-hemophilic factor (AHF). In humans, factor VIII is encoded by the ''F8'' gene. Defects in this gene result in hemophilia A, a recessive X-linked coagulation disorder. ...
concentration and rarer inherited coagulation
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism o ...
abnormalities.
Diagnosis
CT pulmonary angiogram
A CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) is a medical diagnostic test that employs computed tomography (CT) angiography to obtain an image of the pulmonary arteries. Its main use is to diagnose pulmonary embolism (PE). It is a preferred choice of imaging i ...
(CTPA) is the preferred method for diagnosis of a pulmonary embolism due to its easy administration and accuracy. Although a CTPA is preferred, there are also other tests that can be done. For example, a proximal lower limb compression ultrasound
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly medical imaging, imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic ultrasound, therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal ...
(CUS) can be used. This is a test which is primarily used as a confirmatory test, meaning it confirms a previous analysis showing the presence or suspected presence of a pulmonary embolism. According to a cross-sectional study, CUS tests have a sensitivity of 41% and specificity of 96%.
If there are concerns this is followed by testing to determine a likelihood of being able to confirm a diagnosis by imaging, followed by imaging if other tests have shown that there is a likelihood of a PE diagnosis.
The diagnosis of PE is based primarily on validated clinical criteria combined with selective testing because the typical clinical presentation (shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing disc ...
, chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
) cannot be definitively differentiated from other causes of chest pain and shortness of breath. The decision to perform medical imaging is based on clinical reasoning, that is, the medical history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is information gained by a physician by asking specific questions, either to the patient or to other peo ...
, symptoms, and findings on physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patien ...
, followed by an assessment of clinical probability.
Probability testing
The most commonly used method to predict clinical probability, the Wells score, is aclinical prediction rule A clinical prediction rule or clinical probability assessment specifies how to use medical signs, symptoms, and other findings to estimate the probability of a specific disease or clinical outcome.
Physicians have difficulty in estimated risks of ...
, whose use is complicated by multiple versions being available. In 1995, Philip Steven Wells
Philip Steven Wells, M.D., M.Sc., FRCPC is a Canadian hematologist and current chair and Chief of Medicine at the University of Ottawa and The Ottawa Hospital. He is considered an expert in thromboembolic disorders and is known for developing the ...
, initially developed a prediction rule (based on a literature search) to predict the likelihood of DVT, based on clinical criteria. A new prediction score for PE was created in 1998 This prediction rule was revised by Wells ''et al.'' in 2000. In the 2000 publication, Wells proposed two different scoring systems using cutoffs of 2 or 4 with the same prediction rule, and also included D-dimer testing in the rule-out of PE in low probability patients. In 2001, Wells published results using the more conservative cutoff of 2 to create three categories. An additional version, the "modified extended version", using the more recent cutoff of 2 but including findings from Wells's initial studies were proposed. Most recently, a further study reverted to Wells's earlier use of a cutoff of 4 points to create only two categories.
There are additional prediction rules for PE, such as the Geneva rule. More importantly, the use of ''any'' rule is associated with reduction in recurrent thromboembolism.
''The Wells score'':
* clinically suspected DVT
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enla ...
– 3.0 points
* alternative diagnosis is less likely than PE – 3.0 points
* tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal (su ...
(heart rate > 100) – 1.5 points
* immobilization (≥ 3d)/surgery in previous four weeks – 1.5 points
* history of DVT
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enla ...
or PE – 1.5 points
* hemoptysis
Hemoptysis is the coughing up of blood or blood-stained mucus from the bronchi, larynx, trachea, or lungs. In other words, it is the airway bleeding. This can occur with lung cancer, infections such as tuberculosis, bronchitis, or pneumonia, and ...
– 1.0 points
* malignancy (with treatment within six months) or palliative – 1.0 points
Traditional interpretation
* Score >6.0 – High (probability 59% based on pooled data)
* Score 2.0 to 6.0 – Moderate (probability 29% based on pooled data)
* Score <2.0 – Low (probability 15% based on pooled data)
Alternative interpretation
* Score > 4 – PE likely. Consider diagnostic imaging.
* Score 4 or less – PE unlikely. Consider D-dimer
D-dimer (or D dimer) is a fibrin degradation product (or FDP), a small protein fragment present in the blood after a blood clot is degraded by fibrinolysis. It is so named because it contains two D fragments of the fibrin protein joined by a cross ...
to rule out PE.
Recommendations for a diagnostic algorithm were published by the PIOPED investigators; however, these recommendations do not reflect research using 64 slice MDCT. These investigators recommended:
* Low clinical probability. If negative D-dimer, PE is excluded. If positive D-dimer, obtain MDCT and base treatment on results.
* Moderate clinical probability. If negative D-dimer, PE is excluded. ''However'', the authors were not concerned that a negative MDCT with negative D-dimer in this setting has a 5% probability of being false. Presumably, the 5% error rate will fall as 64 slice MDCT is more commonly used. If positive D-dimer, obtain MDCT and base treatment on results.
* High clinical probability. Proceed to MDCT. If positive, treat, if negative, more tests are needed to exclude PE. A D-dimer of less than 750 ug/L does not rule out PE in those who are at high risk.
Pulmonary embolism rule-out criteria
The pulmonary embolism rule-out criteria (PERC) helps assess people in whom pulmonary embolism is suspected, but unlikely. Unlike the Wells score andGeneva score
The Geneva score is a clinical prediction rule used in determining the pre-test probability of pulmonary embolism (PE) based on a patient's risk factors and clinical findings. It has been shown to be as accurate as the Wells Score, and is less rel ...
, which are clinical prediction rules intended to risk stratify people with suspected PE, the PERC rule is designed to rule out the risk of PE in people when the physician has already stratified them into a low-risk category.
People in this low risk category without any of these criteria may undergo no further testing for PE: low oxygen saturations – SaO2 <95%, unilateral leg swelling, coughing up blood, prior DVT or PE, recent surgery or trauma, age >50, hormone use, fast heart rate. The rationale behind this decision is that further testing (specifically CT angiogram of the chest) may cause more harm (from radiation exposure and contrast dye) than the risk of PE. The PERC rule has a sensitivity of 97.4% and specificity of 21.9% with a false negative rate of 1.0% (16/1666).
Blood tests
In people with a low or moderate suspicion of PE, a normalD-dimer
D-dimer (or D dimer) is a fibrin degradation product (or FDP), a small protein fragment present in the blood after a blood clot is degraded by fibrinolysis. It is so named because it contains two D fragments of the fibrin protein joined by a cross ...
level (shown in a blood test
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cholester ...
) is enough to exclude the possibility of thrombotic PE, with a three-month risk of thromboembolic events being 0.14%. D-dimer is highly sensitive but not specific (specificity around 50%). In other words, a positive D-dimer is not synonymous with PE, but a negative D-dimer is, with a good degree of certainty, an indication of absence of a PE. A low pretest probability is also valuable in ruling out PE. The typical cut off is 500 μg/L, although this varies based on the assay. However, in those over the age of 50, changing the cut-off value to the person's age multiplied by 10 μg/L (accounting for assay which has been used) is recommended as it decreases the number of falsely positive tests without missing any additional cases of PE.
When a PE is being suspected, several blood test
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cholester ...
s are done in order to exclude important secondary causes of PE. This includes a full blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cells and plat ...
, clotting status ( PT, aPTT
The partial thromboplastin time (PTT), also known as the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT or APTT), is a blood test that characterizes coagulation of the blood. A historical name for this measure is the kaolin-cephalin clotting time ( ...
, TT), and some screening tests (erythrocyte sedimentation rate
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR or sed rate) is the rate at which red blood cells in anticoagulated whole blood descend in a standardized tube over a period of one hour. It is a common hematology test, and is a non-specific measure of ...
, kidney function
Assessment of kidney function occurs in different ways, using the presence of symptoms and signs, as well as measurements using urine tests, blood tests, and medical imaging.
Functions of a healthy kidney include maintaining a person's fluid ...
, liver enzyme
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial thromboplastin ti ...
s, electrolyte
An electrolyte is a medium containing ions that is electrically conducting through the movement of those ions, but not conducting electrons. This includes most soluble salts, acids, and bases dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water. Upon dis ...
s). If one of these is abnormal, further investigations might be warranted to the issue.
Troponin
image:Troponin Ribbon Diagram.png, 400px, Ribbon representation of the human cardiac troponin core complex (52 kDa core) in the calcium-saturated form. Blue = troponin C; green = troponin I; magenta = troponin T.; ; rendered with PyMOL
Troponin, ...
levels are increased in between 16 and 47% with pulmonary embolism.
Imaging
In typical people who are not known to be at high risk of PE, imaging is helpful to confirm or exclude a diagnosis of PE after simpler first-line tests are used. Medical societies recommend tests such as theD-dimer
D-dimer (or D dimer) is a fibrin degradation product (or FDP), a small protein fragment present in the blood after a blood clot is degraded by fibrinolysis. It is so named because it contains two D fragments of the fibrin protein joined by a cross ...
to first provide supporting evidence for the need for imaging, and imaging would be done if other tests confirmed a moderate or high probability of finding evidence to support a diagnosis of PE.
CT pulmonary angiography
A CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) is a medical diagnostic test that employs computed tomography (CT) angiography to obtain an image of the pulmonary arteries. Its main use is to diagnose pulmonary embolism (PE). It is a preferred choice of imaging i ...
is the recommended first line diagnostic imaging test in most people.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequency, frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing range, hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hea ...
of the legs can confirm the presence of a PE but cannot rule it out.
CT pulmonary angiography
CT pulmonary angiography
A CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) is a medical diagnostic test that employs computed tomography (CT) angiography to obtain an image of the pulmonary arteries. Its main use is to diagnose pulmonary embolism (PE). It is a preferred choice of imaging i ...
(CTPA) is a pulmonary angiogram obtained using computed tomography (CT) with radiocontrast
Radiocontrast agents are substances used to enhance the visibility of internal structures in X-ray-based imaging techniques such as computed tomography (contrast CT), projectional radiography, and fluoroscopy. Radiocontrast agents are typically io ...
rather than right heart catheterization. Its advantages are that it is accurate, it is non-invasive, it is more often available, and it may identifying other lung disorders in case there is no pulmonary embolism. The accuracy and non-invasive nature of CTPA also make it advantageous for people who are pregnant.
CT pulmonary angiography
A CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) is a medical diagnostic test that employs computed tomography (CT) angiography to obtain an image of the pulmonary arteries. Its main use is to diagnose pulmonary embolism (PE). It is a preferred choice of imaging i ...
showing a "saddle embolus" at the bifurcation of the main pulmonary artery and thrombus burden in the lobar arteries on both sides.
File:CT of lung infarction with reverse halo sign, annotated.png, Pulmonary embolism (white arrow) that has been long-standing and has caused a lung infarction (black arrow) seen as a reverse halo sign.
cohort study
A cohort study is a particular form of longitudinal study that samples a cohort (a group of people who share a defining characteristic, typically those who experienced a common event in a selected period, such as birth or graduation), performing ...
, single-slice spiral CT
X-ray computed tomography operates by using an X-ray generator that rotates around the object; X-ray detectors are positioned on the opposite side of the circle from the X-ray source.
A visual representation of the raw data obtained is called ...
may help diagnose detection among people with suspected pulmonary embolism. In this study, the sensitivity was 69% and specificity was 84%. In this study which had a prevalence of detection was 32%, the positive predictive value
The positive and negative predictive values (PPV and NPV respectively) are the proportions of positive and negative results in statistics and diagnostic tests that are true positive and true negative results, respectively. The PPV and NPV descr ...
of 67.0% and negative predictive value
The positive and negative predictive values (PPV and NPV respectively) are the proportions of positive and negative results in statistics and diagnostic tests that are true positive and true negative results, respectively. The PPV and NPV descr ...
of 85.2%. However, this study's results may be biased due to possible incorporation bias, since the CT scan was the final diagnostic tool in people with pulmonary embolism. The authors noted that a negative single slice CT scan is insufficient to rule out pulmonary embolism on its own. A separate study with a mixture of 4 slice and 16 slice scanners reported a sensitivity of 83% and a specificity of 96%, which means that it is a good test for ruling out a pulmonary embolism if it is not seen on imaging and that it is very good at confirming a pulmonary embolism is present if it is seen. This study noted that additional testing is necessary when the clinical probability is inconsistent with the imaging results. CTPA is non-inferior to VQ scanning, and identifies more emboli (without necessarily improving the outcome) compared to VQ scanning.
Ventilation/perfusion scan
 A
A ventilation/perfusion scan
A ventilation/perfusion lung scan, also called a V/Q lung scan, or ventilation/perfusion scintigraphy, is a type of medical imaging using scintigraphy and medical isotopes to evaluate the circulation of air and blood within a patient's lungs, in ...
(or V/Q scan or lung scintigraphy
Scintigraphy (from Latin ''scintilla'', "spark"), also known as a gamma scan, is a diagnostic test in nuclear medicine, where radioisotopes attached to drugs that travel to a specific organ or tissue (radiopharmaceuticals) are taken internally and ...
) shows that some areas of the lung are being ventilated but not perfused with blood (due to obstruction by a clot). This type of examination is as accurate as multislice CT, but is less used, due to the greater availability of CT technology. It is particularly useful in people who have an allergy to iodinated contrast
Iodinated contrast is a form of intravenous radiocontrast agent containing iodine, which enhances the visibility of vascular structures and organs during radiographic procedures. Some pathologies, such as cancer, have particularly improved visibil ...
, impaired kidney function, or are pregnant
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestation, gestates) inside a woman, woman's uterus (womb). A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occur ...
(due to its lower radiation exposure as compared to CT). The test can be performed with planar two-dimensional imaging, or single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT
Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT, or less commonly, SPET) is a nuclear medicine tomographic imaging technique using gamma rays. It is very similar to conventional nuclear medicine planar imaging using a gamma camera (that is, ...
) which enables three-dimensional imaging. Hybrid devices combining SPECT and CT (SPECT/CT) further enable anatomic characterization of any abnormality.
Low probability diagnostic tests/non-diagnostic tests
Tests that are frequently done that are not sensitive for PE, but can be diagnostic. *Chest X-ray
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in med ...
s are often done on people with shortness of breath to help rule-out other causes, such as congestive heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, a ...
and rib fracture
A rib fracture is a break in a rib bone. This typically results in chest pain that is worse with inspiration. Bruising may occur at the site of the break. When several ribs are broken in several places a flail chest results. Potential complicatio ...
. Chest X-rays in PE are rarely normal, but usually lack sign
A sign is an object, quality, event, or entity whose presence or occurrence indicates the probable presence or occurrence of something else. A natural sign bears a causal relation to its object—for instance, thunder is a sign of storm, or me ...
s that suggest the diagnosis of PE (for example, Westermark sign
In chest radiography, the Westermark sign is a sign that represents a focus of oligemia (hypovolemia) (leading to collapse of vessel) seen distal to a pulmonary embolism (PE). While the chest x-ray is normal in the majority of PE cases, the Westerm ...
, Hampton's hump
Hampton's hump, also called Hampton hump, is a radiologic sign which consists of a shallow wedge-shaped opacity in the periphery of the lung with its base against the pleural surface. It is named after Aubrey Otis Hampton, who first described it ...
).
* Ultrasonography
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies fr ...
of the legs, also known as leg doppler, in search of deep venous thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enla ...
(DVT). The presence of DVT, as shown on ultrasonography
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies fr ...
of the legs, is in itself enough to warrant anticoagulation, without requiring the V/Q or spiral CT scans (because of the strong association between DVT and PE). This may be a valid approach in pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ca ...
, in which the other modalities would increase the risk of birth defects in the unborn child. However, a negative scan does not rule out PE, and low-radiation dose scanning may be required if the mother is deemed at high risk of having a pulmonary embolism. The main use of ultrasonography of the legs is therefore in those with clinical symptoms suggestive of deep vein thrombosis.
Fluoroscopic pulmonary angiography
gold standard
A gold standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the early 1920s, and from the la ...
for diagnosis was pulmonary angiography
Pulmonary angiography (or pulmonary arteriography,conventional pulmonary angiography, selective pulmonary angiography) is a medical fluoroscopic procedure used to visualize the pulmonary arteries and much less frequently, the pulmonary veins. It ...
by fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy () is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope () allows a physician to see the internal structure and functio ...
, but this has fallen into disuse with the increased availability of non-invasive techniques that offer similar diagnostic accuracy.
Electrocardiogram
 The primary use of the ECG is to rule out other causes of chest pain. An electrocardiogram (ECG) is routinely done on people with chest pain to quickly diagnose
The primary use of the ECG is to rule out other causes of chest pain. An electrocardiogram (ECG) is routinely done on people with chest pain to quickly diagnose myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may ...
s (heart attacks), an important differential diagnosis in an individual with chest pain. While certain ECG changes may occur with PE, none are specific enough to confirm or sensitive enough to rule out the diagnosis. An ECG may show signs of right heart strain
Right heart strain (also right ventricular strain or RV strain) is a medical finding of right ventricular dysfunction where the heart muscle of the right ventricle (RV) is deformed. Right heart strain can be caused by pulmonary hypertension, pulm ...
or acute cor pulmonale
Pulmonary heart disease, also known as cor pulmonale, is the enlargement and failure of the right ventricle of the heart as a response to increased vascular resistance (such as from pulmonic stenosis) or high blood pressure in the lungs.
Chronic ...
in cases of large PEs – the classic signs are a large S wave in lead I, a large Q wave in lead III, and an inverted T wave
In electrocardiography, the T wave represents the repolarization of the ventricles. The interval from the beginning of the QRS complex to the apex of the T wave is referred to as the ''absolute refractory period''. The last half of the T wave ...
in lead III (S1Q3T3), which occurs in 12–50% of people with the diagnosis, yet also occurs in 12% without the diagnosis.
This is occasionally present (occurring in up to 20% of people), but may also occur in other acute lung conditions, and, therefore, has limited diagnostic value. The most commonly seen signs in the ECG are sinus tachycardia
Sinus tachycardia is an elevated sinus rhythm characterized by an increase in the rate of electrical impulses arising from the sinoatrial node. In adults, sinus tachycardia is defined as a heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute (bpm). The ...
, right axis deviation, and right bundle branch block
A right bundle branch block (RBBB) is a heart block in the right bundle branch of the electrical conduction system.
During a right bundle branch block, the right ventricle is not directly activated by impulses travelling through the right bu ...
. Sinus tachycardia, however, is still only found in 8–69% of people with PE.
ECG findings associated with pulmonary emboli may suggest worse prognosis since the six findings identified with RV strain on ECG (heart rate > 100 beats per minute, S1Q3T3, inverted T waves in leads V1-V4, ST elevation in aVR, complete right bundle branch block, and atrial fibrillation) are associated with increased risk of circulatory shock and death.
Cases with inverted T in leads V1-3 are suspected with PE or inferior myocardial infarction. PE cases show inverted T waves in leads II and aVF, but inferior myocardial infarction cases do not show inverted T waves in II and aVF.
Echocardiography
In massive and submassive PE, dysfunction of the right side of the heart may be seen onechocardiography
An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart.
It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound.
Echocardiography has become routinely used in t ...
, an indication that the pulmonary artery
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and t ...
is severely obstructed and the right ventricle
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper ...
, a low-pressure pump, is unable to match the pressure. Some studies (see below) suggest that this finding may be an indication for thrombolysis
Thrombolysis, also called fibrinolytic therapy, is the breakdown (lysis) of blood clots formed in blood vessels, using medication. It is used in ST elevation myocardial infarction, stroke, and in cases of severe venous thromboembolism (massive p ...
. Not every person with a (suspected) pulmonary embolism requires an echocardiogram, but elevations in cardiac troponins or brain natriuretic peptide
Brain natriuretic peptide 32 (BNP), also known as B-type natriuretic peptide, is a hormone secreted by cardiomyocytes in the heart ventricles in response to stretching caused by increased ventricular blood volume. Along with NT-proBNP, BNP is on ...
may indicate heart strain and warrant an echocardiogram, and be important in prognosis.
The specific appearance of the right ventricle on echocardiography is referred to as the ''McConnell's sign''. This is the finding of akinesia of the mid-free wall but a normal motion of the apex. This phenomenon has a 77% sensitivity and a 94% specificity for the diagnosis of acute pulmonary embolism in the setting of right ventricular dysfunction.

Prevention
Pulmonary embolism may be preventable in those with risk factors. People admitted to hospital may receive preventative medication, including unfractionatedheparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Since heparins depend on the activity of antithrombin, they are considered anticoagulants. Specifically it is also used in the treatm ...
, low molecular weight heparin
Low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) is a class of anticoagulant medications. They are used in the prevention of blood clots and treatment of venous thromboembolism (deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism) and in the treatment of myocardial in ...
(LMWH), or fondaparinux
Fondaparinux (trade name Arixtra) is an anticoagulant medication chemically related to low molecular weight heparins. It is marketed by GlaxoSmithKline. A generic version developed by Alchemia is marketed within the US by Dr. Reddy's Laboratories.
...
, and anti-thrombosis stockings to reduce the risk of a DVT in the leg that could dislodge and migrate to the lungs.
Following the completion of anticoagulation in those with prior PE, long-term aspirin is useful to prevent recurrence.
Treatment
Anticoagulant therapy is the mainstay of treatment. Acutely, supportive treatments, such asoxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
or analgesia
Pain management is an aspect of medicine and health care involving relief of pain (pain relief, analgesia, pain control) in various dimensions, from acute and simple to chronic and challenging. Most physicians and other health professionals ...
, may be required. People are often admitted to hospital in the early stages of treatment, and tend to remain under inpatient care until the INR has reached therapeutic levels (if warfarin is used). Increasingly, however, low-risk cases are managed at home in a fashion already common in the treatment of DVT. Evidence to support one approach versus the other is weak.
Anticoagulation
Anticoagulant therapy is the mainstay of treatment. For many years,vitamin K antagonist
Vitamin K antagonists (VKA) are a group of substances that reduce blood clotting by reducing the action of vitamin K. The term "vitamin K antagonist" is technically a misnomer, as the drugs do not directly antagonise the action of vitamin K in t ...
s (warfarin or less commonly acenocoumarol
Acenocoumarol is an anticoagulant that functions as a vitamin K antagonist (like warfarin). It is a derivative of coumarin
Coumarin () or 2''H''-chromen-2-one is an aromatic organic chemical compound with formula . Its molecule can be descri ...
or phenprocoumon
Phenprocoumon (marketed under the brand names Marcoumar, Marcumar and Falithrom) is a long-acting blood thinner drug to be taken by mouth, and a derivative of coumarin. It acts as a vitamin K antagonist and inhibits blood clotting (coagulation) b ...
) have been the cornerstone. As vitamin K antagonists do not act immediately, initial treatment is with rapidly acting injectable anticoagulants: unfractionated heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Since heparins depend on the activity of antithrombin, they are considered anticoagulants. Specifically it is also used in the treatm ...
(UFH), low molecular weight heparin
Low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) is a class of anticoagulant medications. They are used in the prevention of blood clots and treatment of venous thromboembolism (deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism) and in the treatment of myocardial in ...
(LMWH), or fondaparinux
Fondaparinux (trade name Arixtra) is an anticoagulant medication chemically related to low molecular weight heparins. It is marketed by GlaxoSmithKline. A generic version developed by Alchemia is marketed within the US by Dr. Reddy's Laboratories.
...
, while oral vitamin K antagonists are initiated and titrated (usually as part of inpatient hospital care) to the international normalized ratio
The prothrombin time (PT) – along with its derived measures of prothrombin ratio (PR) and international normalized ratio (INR) – is an assay for evaluating the ''extrinsic'' pathway and common pathway of coagulation. This blood test is als ...
, a test that determines the dose. In terms of injectable treatments, LMWH may reduce bleeding among people with pulmonary embolism as compared to UFH. According to the same review, LMWH reduced the incidence of recurrent thrombotic complications and reduced thrombus size when compared to heparin. There was no difference in overall mortality between participants treated with LMWH and those treated with unfractionated heparin. Vitamin K antagonists require frequent dose adjustment and monitoring of the international normalized ratio
The prothrombin time (PT) – along with its derived measures of prothrombin ratio (PR) and international normalized ratio (INR) – is an assay for evaluating the ''extrinsic'' pathway and common pathway of coagulation. This blood test is als ...
(INR). In PE, INRs between 2.0 and 3.0 are generally considered ideal. If another episode of PE occurs under warfarin treatment, the INR window may be increased to e.g. 2.5–3.5 (unless there are contraindications) or anticoagulation may be changed to a different anticoagulant e.g. LMWH.
In recent years, many anticoagulants have been introduced that offer similar to warfarin but without a need for titration to the INR. Known as the directly acting oral anticoagulants
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where the ...
, these treatments are now preferred over vitamin K antagonists by American professional guidelines. Two of these (rivaroxaban
Rivaroxaban, sold under the brand name Xarelto among others, is an anticoagulant medication (blood thinner) used to treat and prevent blood clots. Specifically it is used to treat deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary emboli and prevent blood clo ...
and apixaban
Apixaban, sold under the brand name Eliquis, is an anticoagulant medication used to treat and prevent blood clots and to prevent stroke in people with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation through directly inhibiting factor Xa. Specifically it is u ...
) do not require initial heparin or fondaparinux treatment, whereas dabigatran
Dabigatran, sold under the brand name Pradaxa among others, is an anticoagulant used to treat and prevent blood clots and to prevent stroke in people with atrial fibrillation. Specifically it is used to prevent blood clots following hip or kne ...
and edoxaban
Edoxaban, sold under the brand name Lixiana among others, is an anticoagulant medication and a direct factor Xa inhibitor. It is taken Oral administration, by mouth.
Compared with warfarin it has fewer drug interactions.
It was developed by ...
do. A Cochrane review found that there is no evidence of a difference between oral DTIs (dabigatran, rivaroxaban, edoxaban, apixaban) and standard anticoagulation in the prevention of recurrent pulmonary embolism.
In people with cancer who develop pulmonary embolism, therapy with a course of LMWH is favored over warfarin or other oral anticoagulants. Similarly, pregnant women are treated with low molecular weight heparin until after delivery to avoid the known teratogenic
Teratology is the study of abnormalities of physiological development in organisms during their life span. It is a sub-discipline in medical genetics which focuses on the classification of congenital abnormalities in dysmorphology. The related t ...
effects of warfarin, especially in the early stages of pregnancy, but it can be used while breastfeeding.
Anticoagulation therapy is usually continued for 3–6 months, or "lifelong" if there have been previous DVTs or PEs, or none of the usual transient risk factors is present. In those without a known cause that can be reversed 2 years of treatment may be better than 6 months. For those with small PEs (known as subsegmental PEs) the effects of anticoagulation is unknown as it has not been properly studied as of 2020.
Thrombolysis
Massive PE causing hemodynamic instability (shock and/or low blood pressure, defined as a systolic blood pressure <90 mmHg or a pressure drop of 40 mmHg for >15 min if not caused by new-onset arrhythmia, hypovolemia or sepsis) is an indication forthrombolysis
Thrombolysis, also called fibrinolytic therapy, is the breakdown (lysis) of blood clots formed in blood vessels, using medication. It is used in ST elevation myocardial infarction, stroke, and in cases of severe venous thromboembolism (massive p ...
, the enzymatic destruction of the clot with medication. In this situation, it is the best available treatment in those without contraindications and is supported by clinical guidelines. It is also recommended in those in cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. It is a medical emergency that, without immediate medical intervention, will result in sudden cardiac death within minutes. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and possib ...
with a known PE. Catheter-directed thrombolysis (CDT) is a new technique found to be relatively safe and effective for massive PEs. This involves accessing the venous system by placing a catheter into a vein in the groin and guiding it through the veins by using fluoroscopic imaging until it is located next to the PE in the lung circulation. Medication that breaks up blood clots is released through the catheter so that its highest concentration is directly next to the pulmonary embolus. CDT is performed by interventional radiologists
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as Fluoroscopy, x-ray fluoroscopy, CT scan, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultraso ...
or vascular surgeons
Vascular surgery is a surgical subspecialty in which diseases of the vascular system, or arteries, veins and lymphatic circulation, are managed by medical therapy, minimally-invasive catheter procedures and surgical reconstruction. The specialty ...
, and in medical centers that offer CDT, it may be offered as a first-line treatment. Catheter-based ultrasound-assisted thrombolysis is being investigated.
The use of thrombolysis in non-massive PEs is still debated. Some have found that the treatment decreases the risk of death and increases the risk of bleeding including intracranial hemorrhage
Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), also known as intracranial bleed, is bleeding within the skull. Subtypes are intracerebral bleeds ( intraventricular bleeds and intraparenchymal bleeds), subarachnoid bleeds, epidural bleeds, and subdural bleeds. ...
. Others have found no decrease in the risk of death.
Inferior vena cava filter
 There are two situations when an
There are two situations when an inferior vena cava filter
An inferior vena cava filter is a medical device made of metal that is implanted by vascular surgeons or interventional radiologists into the inferior vena cava to
prevent a life-threatening pulmonary embolism (PE) or venous thromboembolism (VT ...
is considered advantageous, and those are if anticoagulant therapy is contraindicated
In medicine, a contraindication is a condition that serves as a reason not to take a certain medical treatment due to the harm that it would cause the patient. Contraindication is the opposite of indication, which is a reason to use a certain tre ...
(e.g. shortly after a major operation), or a person has a pulmonary embolus in spite of being anticoagulated. In these instances, it may be implanted to prevent new or existing DVTs from entering the pulmonary artery and combining with an existing blockage. In spite of the device's theoretical advantage of preventing pulmonary emboli, there is a lack of evidence supporting its effectiveness.
Inferior vena cava filters should be removed as soon as it becomes safe to start using anticoagulation. Although modern filters are meant to be retrievable, complications may prevent some from being removed. The long-term safety profile of permanently leaving a filter inside the body is not known.
Surgery
Surgical management of acute pulmonary embolism (pulmonary thrombectomy
A pulmonary thrombectomy is an emergency surgical procedure used to remove blood clots from the pulmonary arteries.
Mechanical thrombectomies can be surgical (surgical thrombectomy) or percutaneous (percutaneous thrombectomy).
Surgical thrombect ...
) is uncommon and has largely been abandoned because of poor long-term outcomes. However, recently, it has gone through a resurgence with the revision of the surgical technique and is thought to benefit certain people. Chronic pulmonary embolism leading to pulmonary hypertension (known as ''chronic thromboembolic hypertension'') is treated with a surgical procedure known as a pulmonary thromboendarterectomy
In thoracic surgery, a pulmonary thromboendarterectomy (PTE), also referred to as pulmonary endarterectomy (PEA), is an operation that removes organized clotted blood (thrombus) from the pulmonary arteries, which supply blood to the lungs.
Indica ...
.
Epidemiology
There are roughly 10 million cases of pulmonary embolisms per year. In the United States, pulmonary embolisms are the primary cause of at least 10,000 to 12,000 deaths per year and a contributing cause in at least 30,000 to 40,000 deaths per year. True incidence involving pulmonary embolisms is unknown because they often go undiagnosed or unnoticed until autopsy. From 1993 to 2012, there have been an increased number of admissions in hospitals due to pulmonary embolisms, jumping from 23 cases per 100,000 people to 65 cases per 100,000 people. Despite this increase, there has been a decrease in mortality during that same time period due to medical advances that have occurred.Venous thromboembolism
Venous thrombosis is blockage of a vein caused by a thrombus (blood clot). A common form of venous thrombosis is deep vein thrombosis (DVT), when a blood clot forms in the deep veins. If a thrombus breaks off (embolizes) and flows to the lungs to ...
(VTE), a common risk factor, is present at much higher rates in those over the age of 70 (three times higher compared to those aged 45 to 69). This is likely due to there being a generally lower level of activity among the elderly, resulting in higher rates of immobility and obesity. VTE has a large, and continuously rising, case fatality rate. This rate is roughly 10% after 30 days, 15% after three months and up to 20% after one year. Pulmonary embolisms alone (when resulting in hospitalizations) have a case fatality rate of about 5% to 10% so VTE can play a large factor in the severity of the embolisms.
When looking at all cases, the rate of fatal pulmonary emboli has declined from 6% to 2% over the last 25 years in the United States. In Europe, an average of approximately 40,000 deaths per year with pulmonary embolism as the primary cause were reported between 2013 and 2015, a conservative estimate because of potential underdiagnosis.
Prognosis
 Fewer than 5 to 10% of symptomatic PEs are fatal within the first hour of symptoms.
There are several markers used for risk stratification and these are also independent predictors of adverse outcomes. These include hypotension, cardiogenic shock, syncope, evidence of right heart dysfunction, and elevated cardiac enzymes. Some ECG changes including S1Q3T3 also correlate with a worse short-term prognosis. There have been other patient-related factors such as
Fewer than 5 to 10% of symptomatic PEs are fatal within the first hour of symptoms.
There are several markers used for risk stratification and these are also independent predictors of adverse outcomes. These include hypotension, cardiogenic shock, syncope, evidence of right heart dysfunction, and elevated cardiac enzymes. Some ECG changes including S1Q3T3 also correlate with a worse short-term prognosis. There have been other patient-related factors such as COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce mu ...
and chronic heart failure thought to also play a role in prognosis.
Prognosis depends on the amount of lung that is affected and on the co-existence of other medical conditions; chronic embolisation to the lung can lead to pulmonary hypertension. After a massive PE, the embolus must be resolved somehow if the patient is to survive. In thrombotic PE, the blood clot may be broken down by fibrinolysis
Fibrinolysis is a process that prevents blood clots from growing and becoming problematic. Primary fibrinolysis is a normal body process, while secondary fibrinolysis is the breakdown of clots due to a medicine, a medical disorder, or some other c ...
, or it may be organized and recanalized so that a new channel forms through the clot. Blood flow is restored most rapidly in the first day or two after a PE. Improvement slows thereafter and some deficits may be permanent. There is controversy over whether small subsegmental PEs need treatment at all and some evidence exists that patients with subsegmental PEs may do well without treatment.
Once anticoagulation is stopped, the risk of a fatal pulmonary embolism is 0.5% per year.
Mortality
Mortality is the state of being mortal, or susceptible to death; the opposite of immortality.
Mortality may also refer to:
* Fish mortality, a parameter used in fisheries population dynamics to account for the loss of fish in a fish stock throug ...
from untreated PEs was said to be 26%. This figure comes from a trial published in 1960 by Barrit and Jordan, which compared anticoagulation against placebo for the management of PE. Barritt and Jordan performed their study in the Bristol Royal Infirmary
The Bristol Royal Infirmary, also known as the BRI, is a large teaching hospital situated in the centre of Bristol, England. It has links with the nearby University of Bristol and the Faculty of Health and Social Care at the University of the Wes ...
in 1957. This study is the only placebo-controlled trial ever to examine the place of anticoagulants in the treatment of PE, the results of which were so convincing that the trial has never been repeated as to do so would be considered unethical. That said, the reported mortality rate of 26% in the placebo group is probably an overstatement, given that the technology of the day may have detected only severe PEs.
Predicting mortality
The PESI and sPESI (= simplified Pulmonary Embolism Severity Index) scoring tools can estimate mortality of patients. The Geneva prediction rules and Wells criteria are used to calculate a pre-test probability of patients to predict who has a pulmonary embolism. These scores are tools to be used with clinical judgment in deciding diagnostic testing and types of therapy. The PESI algorithm comprises 11 routinely available clinical variables. It puts the subjects into one of five classes (I–V), with 30-day mortality ranging from 1.1% to 24.5%. Those in classes I and II are low-risk and those in classes III–V are high-risk.References
External links
*Wells criteria for pulmonary embolism online calculator
Clinical prediction website – Wells criteria for pulmonary embolism
* * {{Authority control Medical emergencies Pulmonary heart disease and diseases of pulmonary circulation Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate